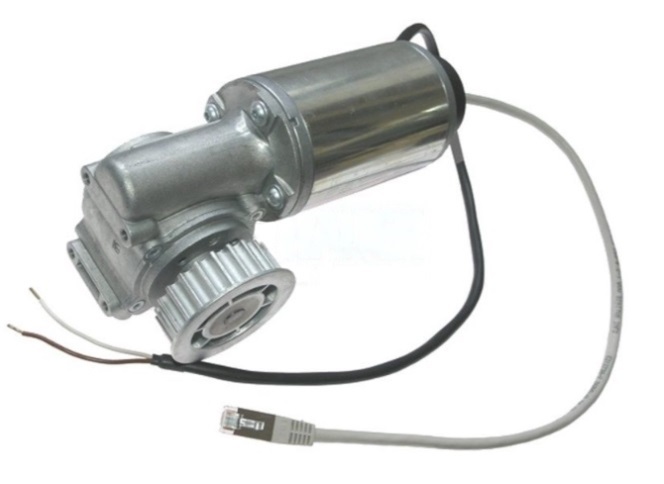
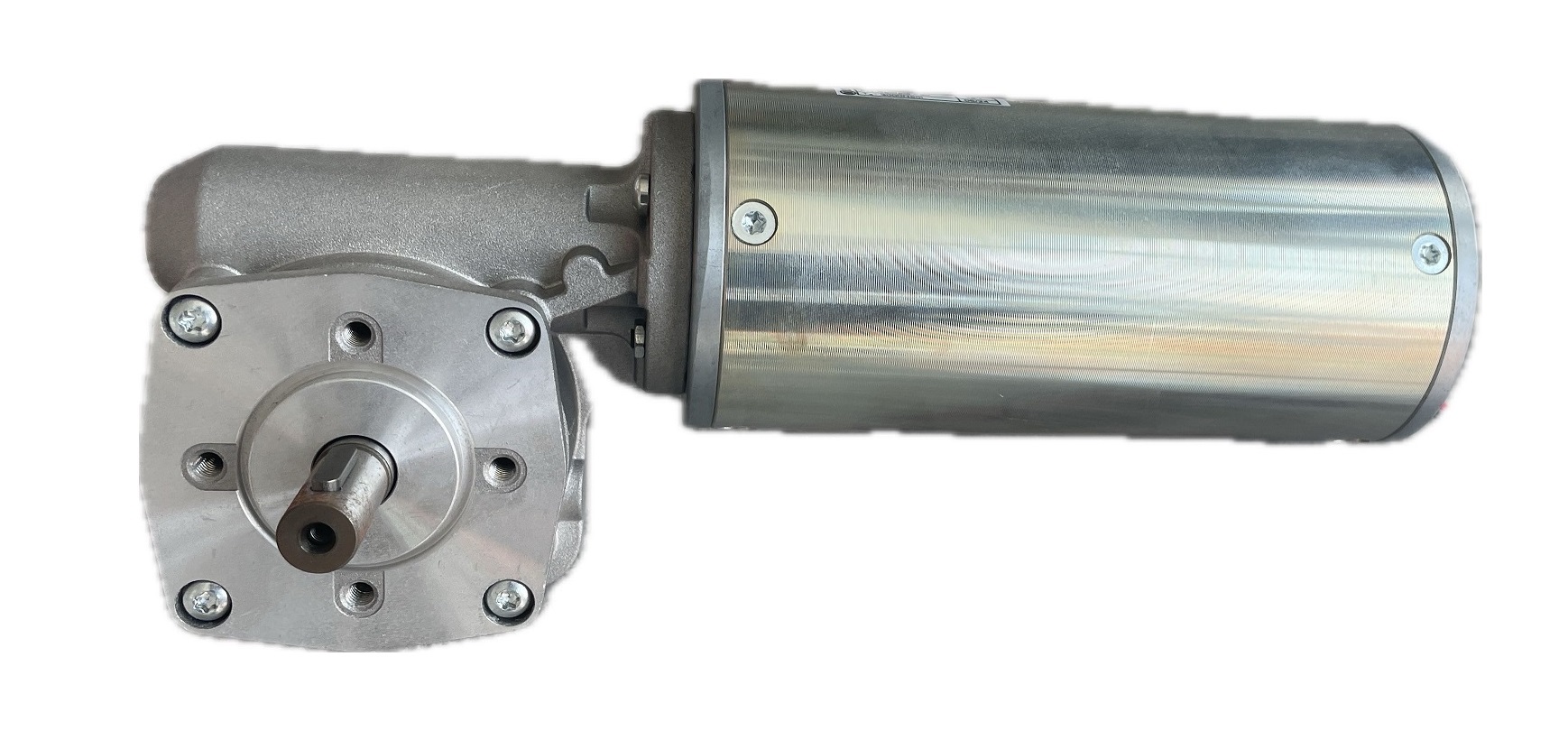
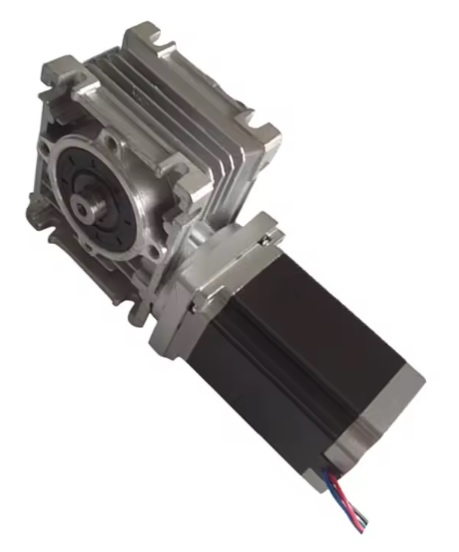
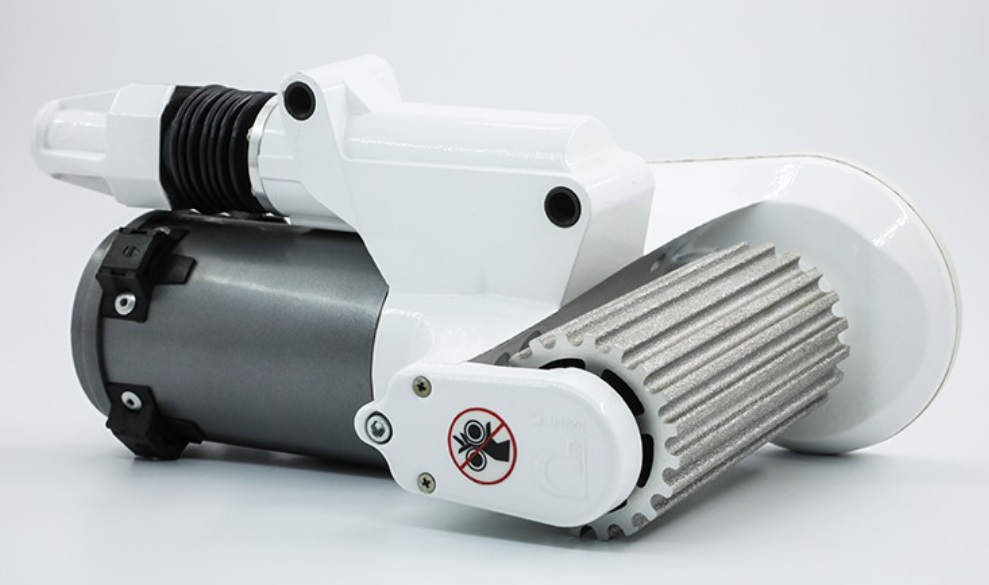
DC Gear Motor Guide
Looking for information about DC gear motors? Learn how these motors operate, their working principles, and the differences between DC gear motors and DC motors. Discover why DC gear motors can overheat and even burn out, including factors such as current, speed, and long-time running. Find out how to prevent burnout and extend the lifespan of your DC gear motor. Get answers to all your questions about DC gear motors and more.
How the DC gear motor operates?
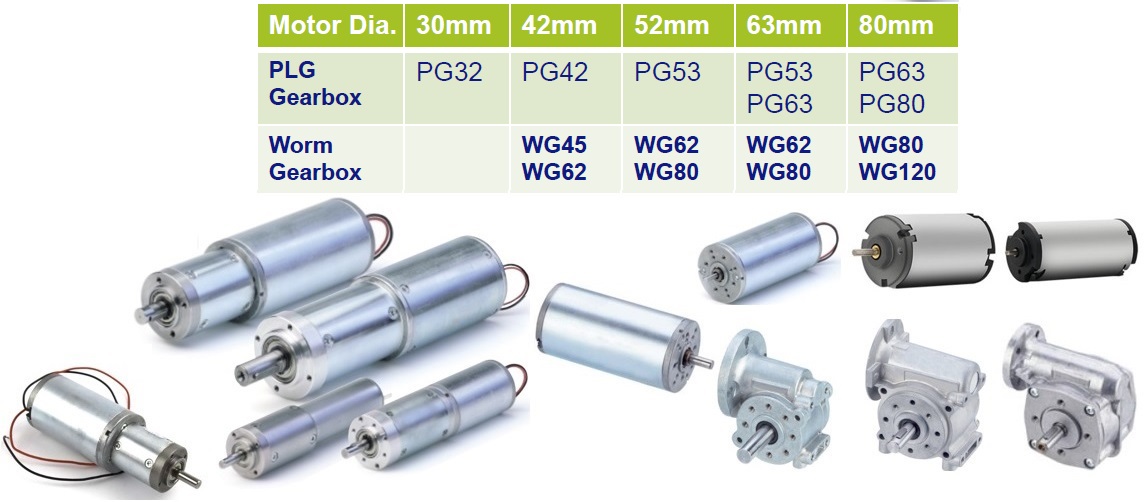
The versatility to produce high torque at low speeds makes the DC gear motors suitable for various applications. It would be great to consider the mode of operation and factors that affect the performance of such devices.

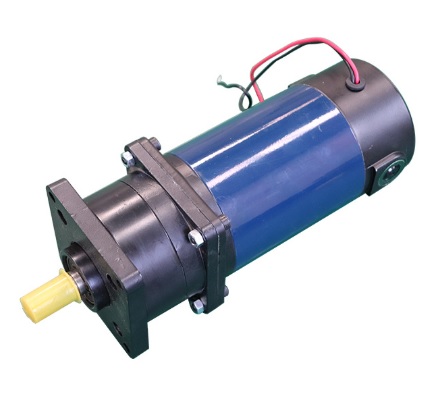
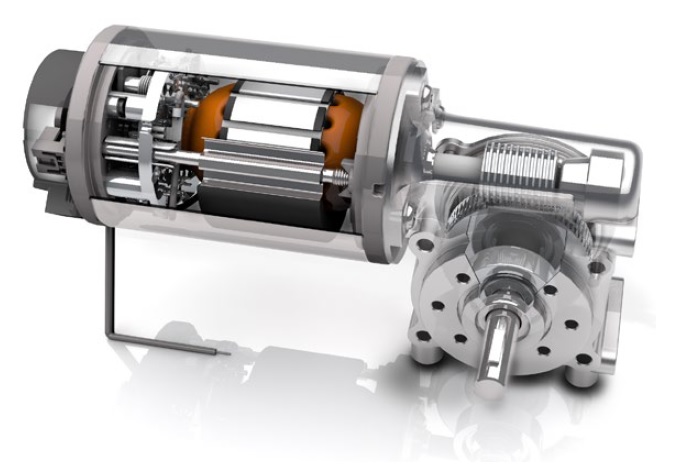
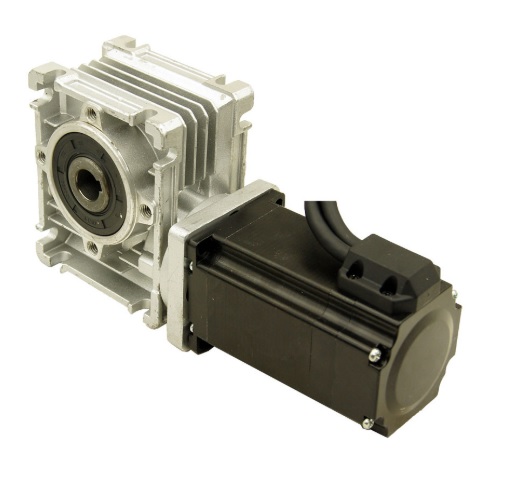
In a DC motor, the shaft connects the first stage gear and the gearbox's first gear. As the DC motor operates, it drives the gears, resulting in the rotation of the output shaft. The rotational power generated by the motor is transmitted through the gear system, allowing for controlled and efficient rotation of the output shaft. This mechanism enables the DC motor to convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, making it a versatile and widely used component in various applications.
The rated torque is the torque that the motor can deliver continuously. In contrast, the max efficiency torque is the maximum torque the motor can deliver when the output shaft is prevented from rotating. Additionally, the voltage and current supplied to the motor can affect its performance, so selecting a motor that can handle the required voltage and current for your application is crucial.
DC gear motor: Understanding the working principle.
The motor comprises a stator, rotor, and commutator. The stator houses electromagnets, the rotor contains permanent magnets, and the commutator is the copper segment. The primary component that enhances the efficiency, i.e., using less energy to generate higher torque of this motor, is the gearbox attached to the output shaft. This energy can power other devices, making DC gear motors versatile and widely used in various applications.
The performance of a DC gear motor is determined by several factors, including the motor's rated torque and stall torque, the voltage and current supplied to the motor, and the design and quality of the gearbox. By selecting the suitable motor and gearbox combination for the application, users can optimize the efficiency and performance of their DC gear motor. By understanding the essential components and their functions, users can select the right DC gear motor for their specific application and achieve optimal performance and efficiency.